Hinge properties
Last reviewed version: 2.18.0The hinges are seen as element decorators in the Decorators window.
Hinge 2
Double click Hinge 2 to enter the Edit hinge-dialogue.
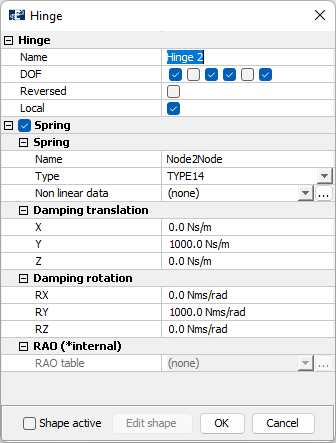
- DOF: here you can select which degrees of freedom that should be restrained or free. The first three checkboxes are translations in x-, y- and z-direction respectively. The three last boxes are rotations about x-, y- and z-direction respectively. By checking a box, the DOF is restrained.
- Reversed: AquaSim has a default node the Hinge is assigned to for each element. If the Hinge is not on the correct side of the element, selecting Reverse will swap the side.
- Local: Hinges can rotate and translate either with respect to the global coordinate system, or the element’s local coordinate system. The bracket should move with respect to the floater pipe, hence Local should be toggled on.
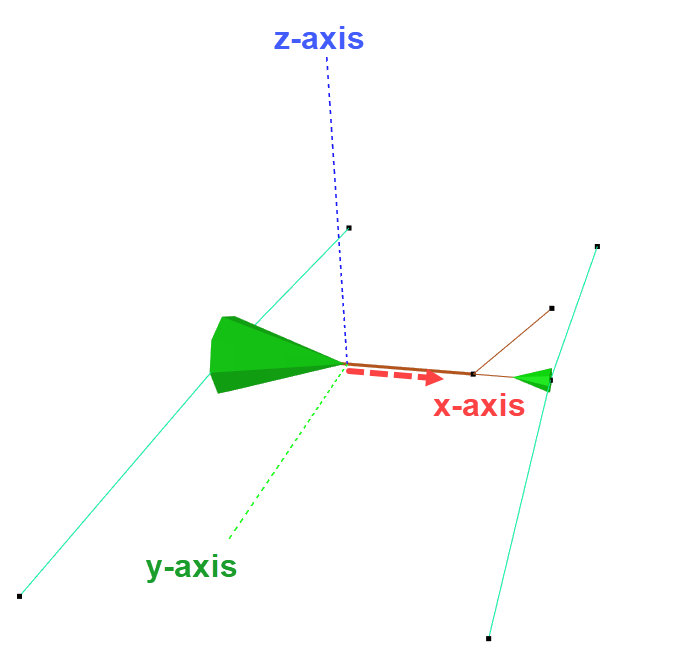
Let us go back to the DOF-section again and see why the checkboxes are selected as they are. Remember that the local x-axis of an element runs from node A to B, and that y- and z-axis are perpendicular to the element. The bracket should be able to translate along and rotate about the local y-axis.
Tips! To see where the local axis run, you can select Normals from the Toolbar and select the bracket-element as shown below.
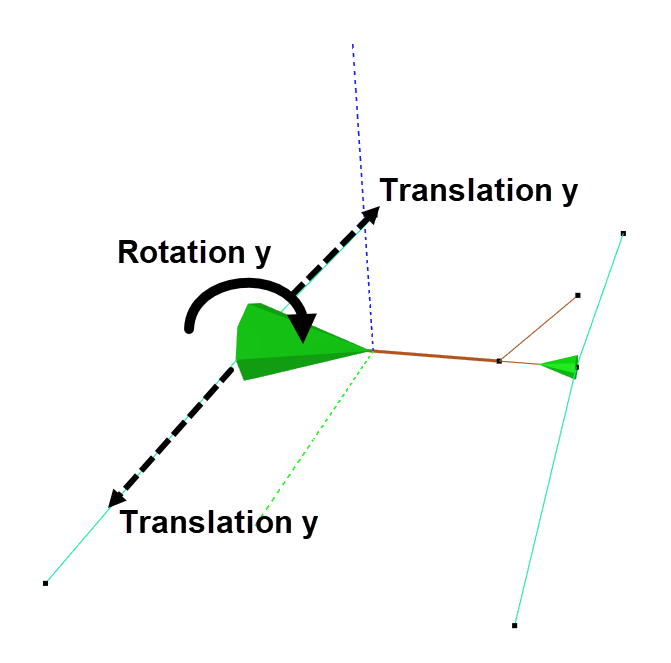
Some friction is assumed between the bracket and the floater. This is included as damping through selecting Spring and Type Type 14. The damping is proportional to the relative velocity between the node and fluid. A damping of 1000Ns/m is introduced for translation in y-direction, and 1000Nms/rad for rotation about y. The size of the damping depends on the friction, and can be determined through e.g., assessing expected distance the bracket should move.
Hinge 1
Double click Hinge 1 in the decorators window.
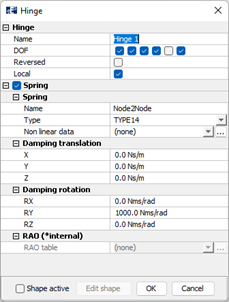
Due to the stoppers, the bracket should only be allowed to rotate about the local y-axis. This is illustrated in the figures below.
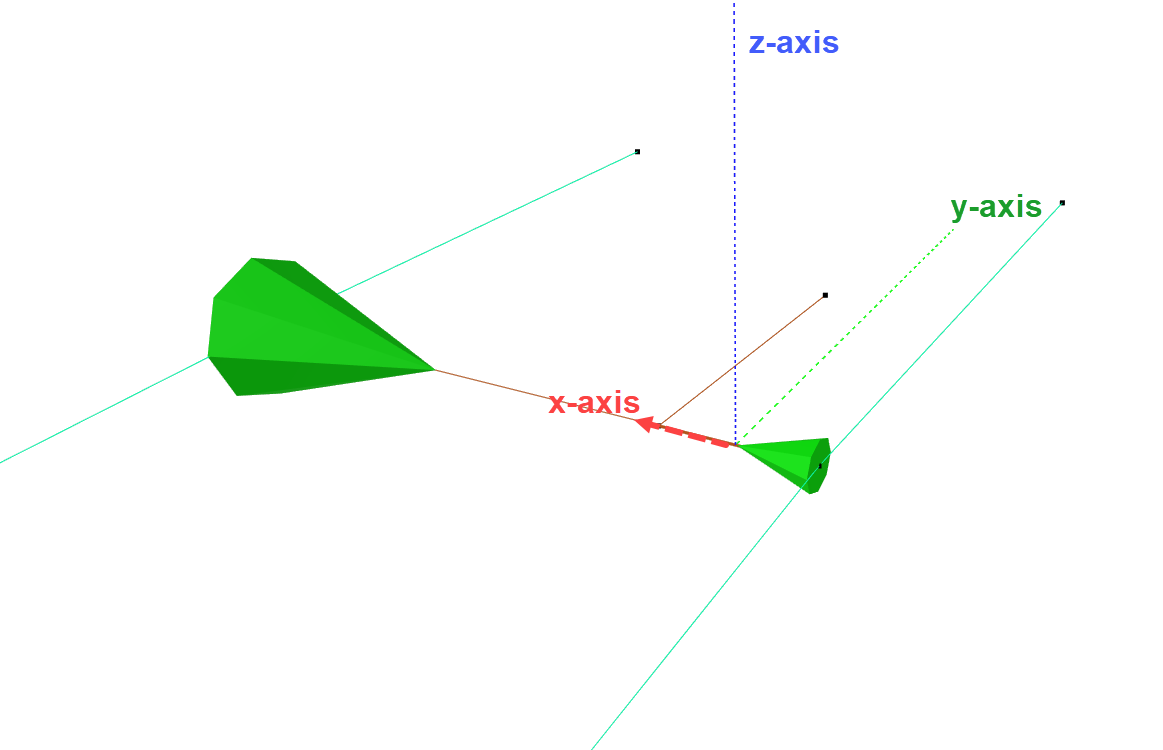
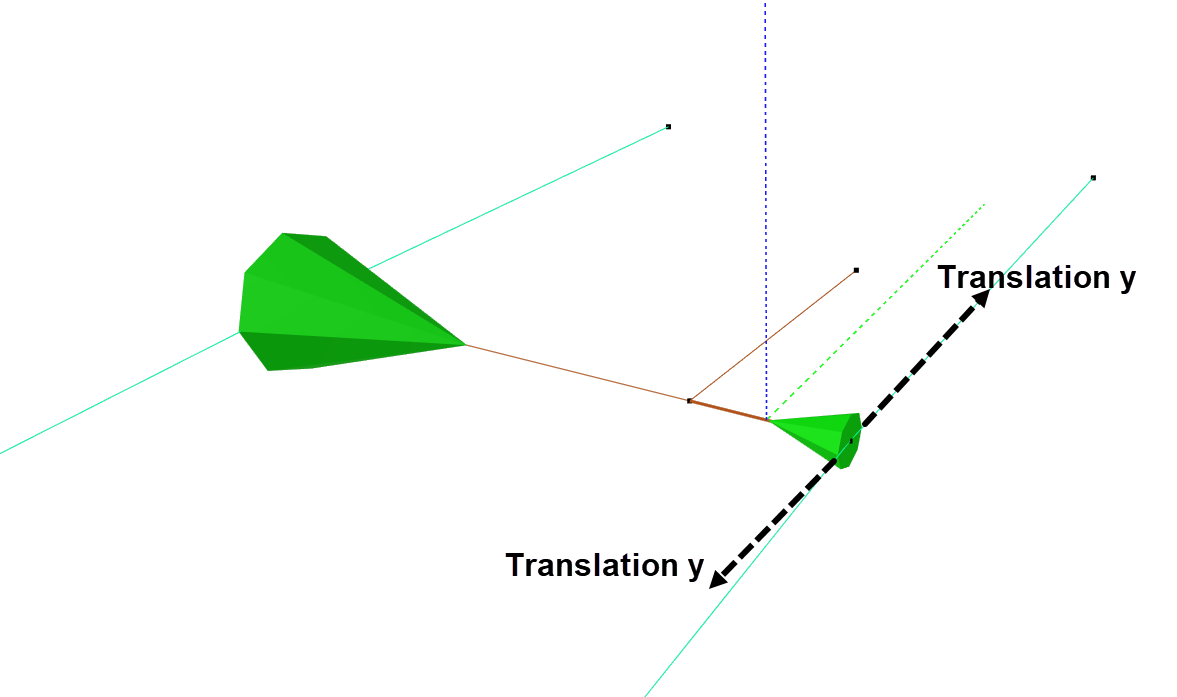
Rotational damping, due to friction, is assigned about the y-axis; 1000 Nms/rad.