Principles of buckling analysis in AquaSim
Last reviewed version: 2.19As from AquaSim version 2.19, buckling analysis is available for the following component types:
- Beam:
- Morison submerged
- Hydrodynamic
- Membrane/ Membrane X:
- Shell
- Normal with bending stiffness
In AquaSim, one has the possibility to apply explicit buckling analyses through the option Buckling /eigen period analysis found in the Export menu. This is illustrated in the figure below.
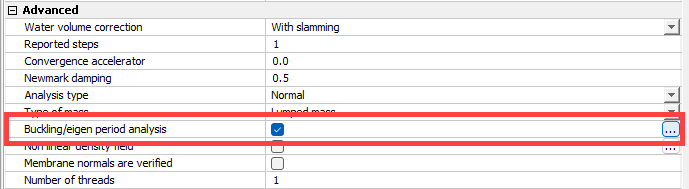
By selecting the three dots […] to the right, one enters the control window for buckling settings.
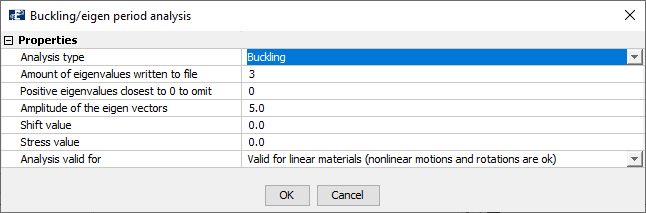
Description of the different options are given in the succeeding sections.
Analysis type
Buckling analysis solves the equation:
$${ K_{\text{elem}} - \delta K_{\text{geom}} = 0 }$$
where \(K_{\text{elem}}\) is the material stiffness for the structural configuration at the given timestep in the analysis. \(K_{\text{geom}}\) is the geometrical stiffness for the structural configuration at the given timestep in the analysis. The result of the analysis is δ, which is the factor the load distribution should linearly be increased to obtain linearized buckling. The corresponding eigen vector is the buckling shape for this factor. Buckling shape may also be referred to as buckling mode, in this tutorial we apply the term buckling shape.
Analysis type provides four different options:
- Buckling: calculation of buckling factor.
- Eigen periods (excluding mass of truss elements): not the topic for this tutorial.
- Eigen periods (including mass of truss elements): not the topic for this tutorial.
- Eigen periods (excluding mass of truss elements and mass caused by nodal loads): not the topic for this tutorial.
Amount of eigenvalues written to files
AquaSim may calculate up to six different buckling factors. In this case, eigen values will correspond to buckling factor. The amount of buckling factors written to file must be a number that is higher than 0 and lower than 7.
If this parameter is equal to 3, then the three buckling shape closes to the Shift value is calculated.
Positive eigenvalues closes to 0 to omit
How many positive buckling factors closest to 0 that shall be omitted in the results written to file.
Amplitude of eigen vectors
The amplitude of buckling shape. The buckling shape indicates the direction of the buckling for the calculated buckling factor. This parameter is unitless and can be interpreted as an amplification factor for the buckling shape. It makes it easier to identify the buckling direction and to evaluate the results.
Shift value
The buckling analysis in AquaSim is conducted by numerical method. This parameter enables a numerical search for buckling factors around this value. I.e. it pinpoints the area in which one whish to find buckling factors.
Stress value
This option is not currently available to use in AquaSim.
Analysis valid for
What type of materials the analysis should be conducted for. Two options are available:
- Valid for linear materials (nonlinear motions and rotations are ok): only material data from Material/ section properties are considered in the analysis. Potential nonlinear relation from NLD-tables is not considered when calculating buckling factors.
- General, but noiser buckling response: materials with both linear and nonlinear relations are included in the buckling analysis. Please note that AquaSim may find numerous of buckling factors when this is selected, and all these can be perceived as “noise”.
Calculations and results
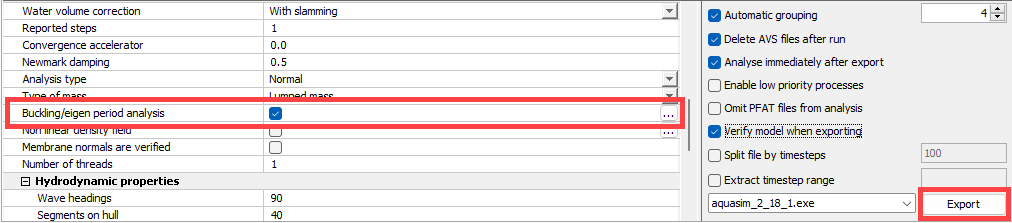
To include buckling study in AquaSim-analysis, the user should select the checkbox for Buckling /eigen period analysis. The user should then export the model and run an analysis as normal, see figure below.
Having carried out an analysis, some additional result files will be generated, they are presented in the figure below.
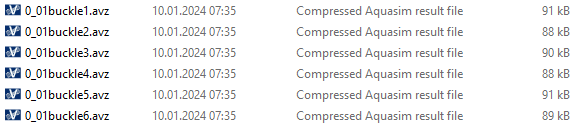
The <filename>buckle1.avz will include the results for the buckling factor closest to Shift value. Please note that each step in the analysis is considered separately, such that each step must be evaluated by the user. The