Post processing static analysis
Last reviewed version: 2.18.0Open the .avz-file in AquaView. Select Results > Displacement > Displacement Z [m]. Select the element as indicated in the figure below (on our model this correspond to element no. 4). Start the playback and observe how the model responds; the horizontal part of the rope close to the seabed will slightly displace upwards in vertical direction, and the float will remain at its initial position.
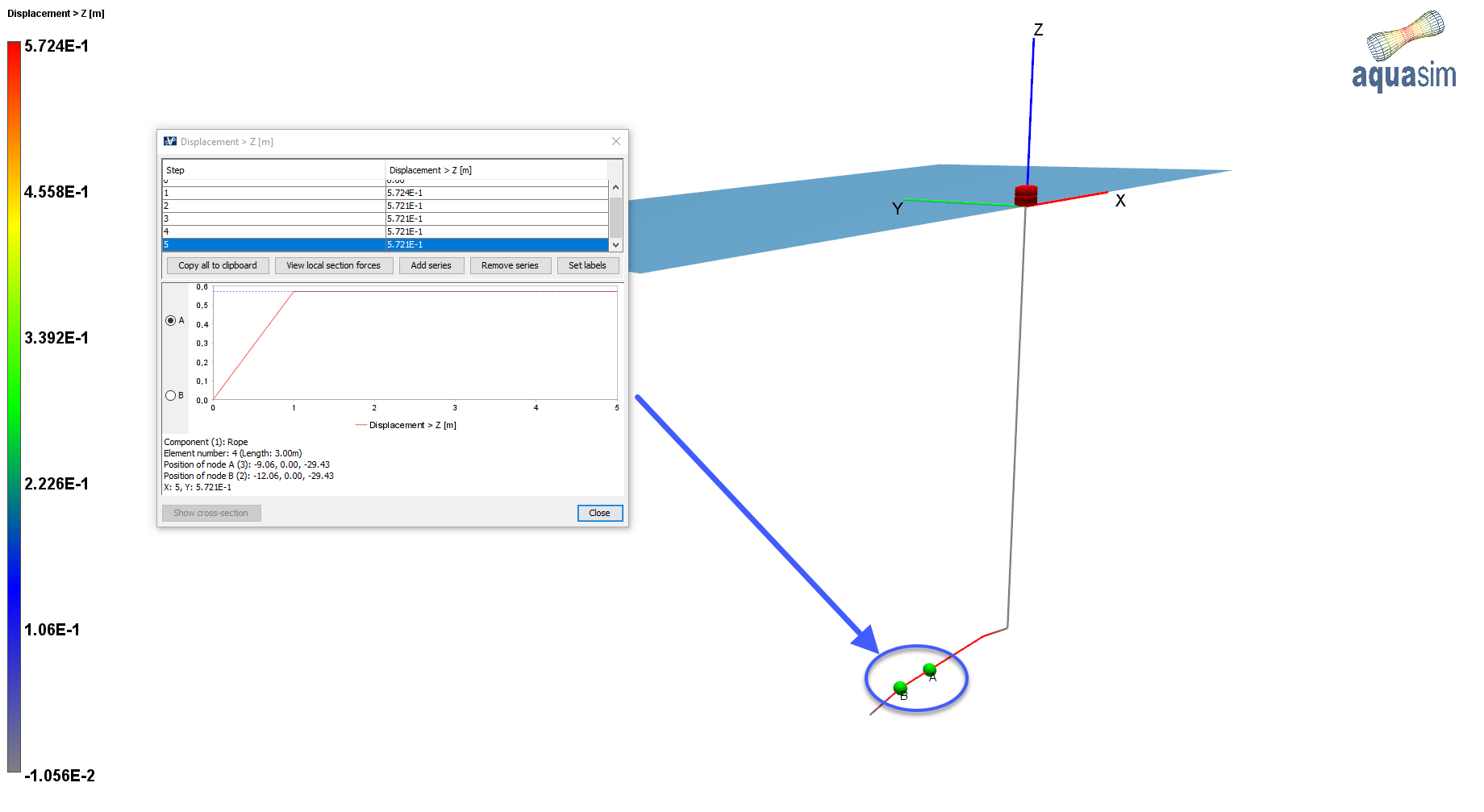
The vertical displacement of the selected node is due to gravitational forces. In our analysis, the displacement is 0.57m in positive z-direction. Theoretically, the displacement is calculated approximately to be:
$${F_z = m \cdot g = 2.5 \frac{kg}{m} \cdot 3m \cdot 9.81 \frac{m}{s^3} = 73.6N}$$
$${r_0 = \sqrt[5]{\frac{F_z}{k_z}} = 0.59m}$$
Where m is the weight of the rope kilograms per meter times the length of element no. 4, which is 3 meters. r_0 is the displacement of node A connected to element no. 4 in z-direction.
The first static considerations are finished. Exit AquaView and return to your model in AquaEdit
Changing Displaced amount
In AquaEdit, re-open the Edit spring-window by double click on the Displaced spring in the Decorators-window. We should now decide that the nodes close to the seabed should not displace below the depth of -30m. In the field Displacement type -0.57 m.

Select OK. The model is now ready for dynamic considerations. Select Export from the Toolbar menu.