Introduction
Last reviewed version: 2.18.0Including contact with the seabed can be useful in many cases, such as when weights are applied in anchoring systems, falling objects and so on. AquaSim provides several options to simulate contact with the seabed. This tutorial presents one way to solve this.
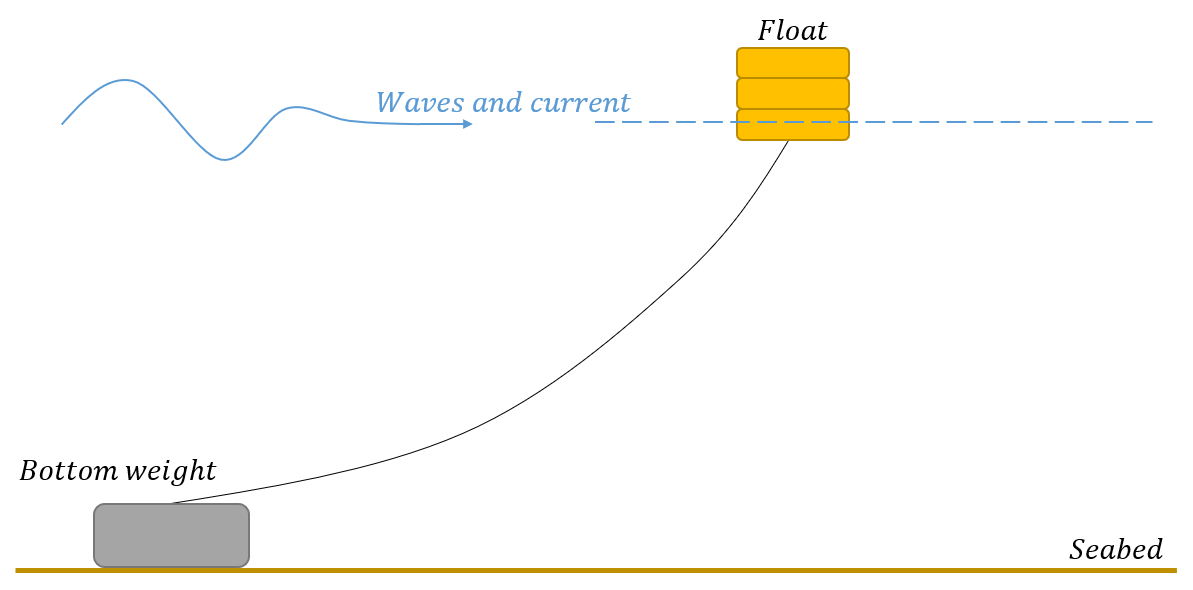
In this case study you will establish a system with a bottom weight, mooring rope, and a float. The float will be exposed to waves and current. When the horizontal force in the rope exceeds the frictional force between the bottom weight and seabed it will start to displace. You are to uncover how much the bottom weight displace during the analysis.
Principles of modelling
Let us discuss the chosen principles of how the system can be modelled in AquaEdit. Other modelling solutions may be applied but is not covered by this tutorial. Before we build the model, we should evaluate the nature of the problem and ‘translate’ this into an AquaSim model; what do we want to achieve with the analysis and which functionality in AquaSim can be used to solve this? How can the problem be simplified to reduce the possibility of errors and divergent results?
To render contact between the bottom weight and seabed, we can examine the possibilities in the Bottom section found in the Export menu. The basic principle of the Bottom section is that the bottom acts as a spring with a spring stiffness. When you select the checkbox for Bottom contact, a flat bottom will be introduced according to the depth specified in Bottom depth.
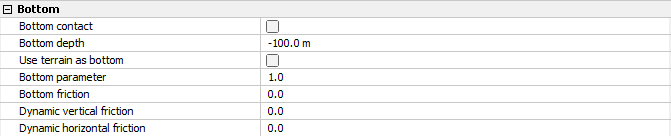
Bottom parameter is the spring stiffness of the seabed, and when nodes displace beneath the defined Bottom depth, the spring stiffness will increase. Bottom friction adds friction to the seabed. Then we have the two last parameters: Dynamic vertical friction and Dynamic horizontal friction. These are constants that are proportional with the velocity of the nodes that are in contact with the seabed and can be interpreted as damping factors. The vertical friction acts in the z-direction, and horizontal friction acts in the xy-plane. *Note
At last, the float may be represented by a spring type Buoy which can be applied to the end-node of the rope situated in the water line.
*Note: If for some reason it is not appropriate to introduce Dynamic friction horizontal/ vertical, one can as an alternative introduce a spring (Type: Dampner) on relevant nodes. This spring works in the same manner as the dynamic friction.