Introduction
Last reviewed version: 2.18.1Using component contact enable to perform analyses where contact and collision between elements are of interest. This can be contact between ship and quay, mooring line contact, falling equipment and so on. AquaSim holds the opportunity to define that there should be contact between selected component groups.
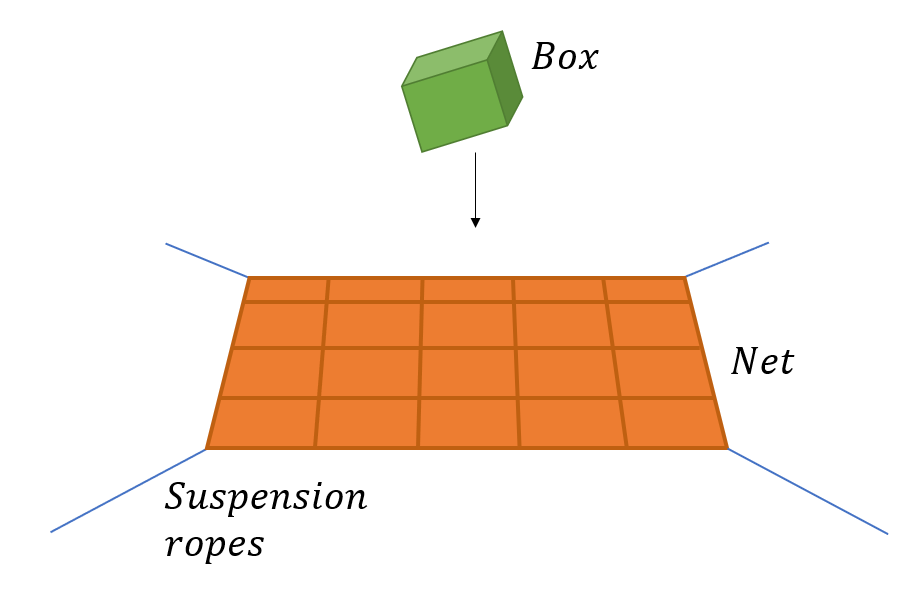
In this case study you will define contact between a falling object and a net. The object could be some sort of box or equipment, and the net could be for safety reasons. When the box hits the net, kinetic energy will be transferred from the box to the net and be distributed to the suspension ropes holding the net. You are to establish a table which defines contact between the box and the net and investigate force and displacement in AquaView.
Principles of Component contact
The basic principle of establishing contact between elements in AquaSim is to first define contact between component groups in AquaEdit. Two-and-two component groups can be assigned contact. From this a Component contact-table is created which defines how the contact should take place.
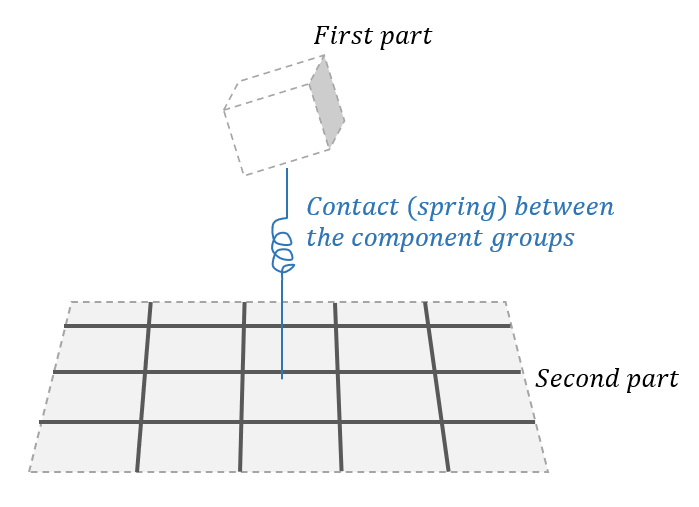
Contact between elements in the component groups is based on a spring, as illustrated in the figure below. We have the following relation between force, spring stiffness and displacement:
$${F = k \cdot r^5 }$$
where F is the contact force, k is the spring stiffness and r is the relative distance between the elements. In addition, you can also assign friction, damping and distance when contact should start.
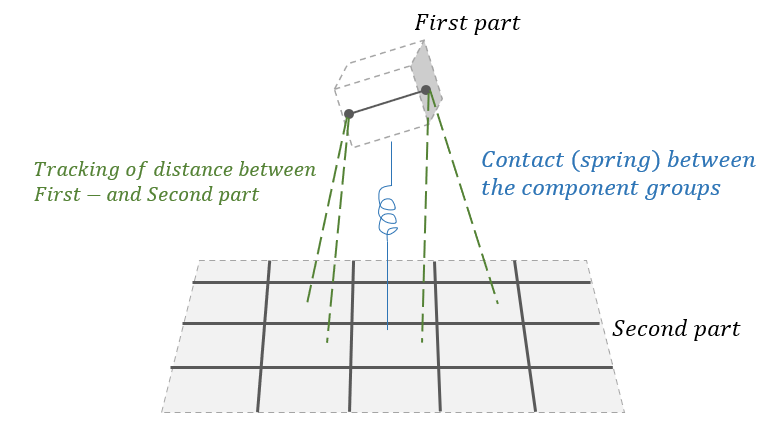
To establish contact, you need to select a “First part” and a “Second part”. The choice of order is for most practical purposes indifferent. AquaSim will keep track of the position and distance between the “First part” and “Second part” in all timesteps in the analysis, this is illustrated in the figure below. If elements in “First part” gets closer to “Second part” than the specified values for where contact is assumed a force will push the elements apart.