Find static equilibrium and validate model AquaView
Last reviewed version: 2.22The system is analyzed with fluid density of 1025 both inside the tarpaulin closed compartment and outside. How the inner water surface height has raised or decreased is found in Result > Impermeable net > Inner height waterline [m].
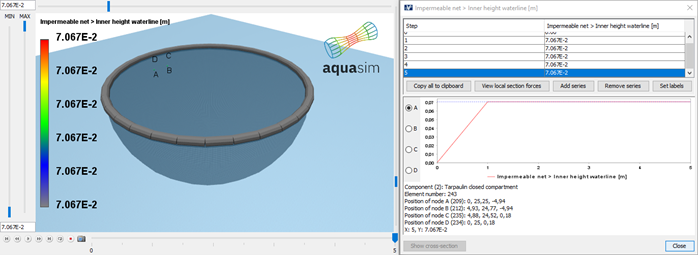
The inner water surface height at static equilibrium is in this case about 7 cm above the outer mean waterline. Having defined a height of 2 meters, this means that the water volume between 2 meters and 7 cm has moved downwards during the analysis.
There are two ways the water can move downwards; the first is that the floater moves downwards with reduced freeboard. The other is that the tarpaulin moves downwards and outwards from stretching. To determine this, one can plot the vertical displacement, Result > Displacement > Displacement Z.
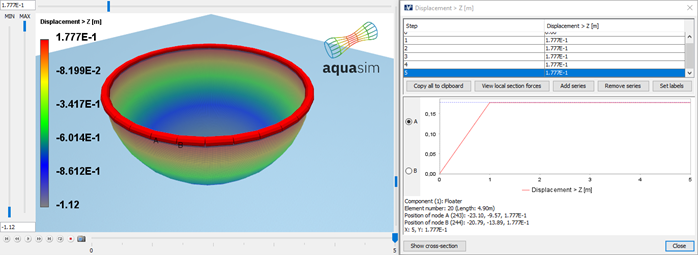
From Figure 19 it is noted that the floater rises by approximately 18 cm, hence the tarpaulin moves downwards from stretching. The bottom part moves approximately 1 meter downwards as shown in Figure 20.
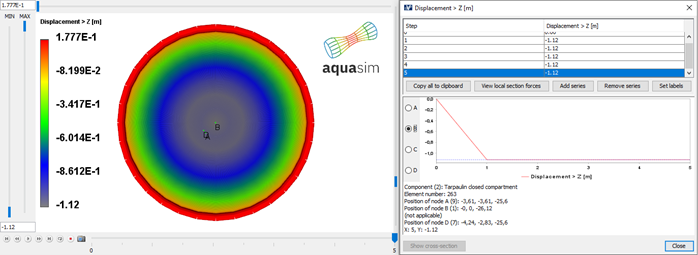
In addition, there is motion horizontally of the tarpaulin. This is about 1 meter, see Figure 21.