Fresh water
Last reviewed version: 2.22If one likes to use a tarpaulin to enclose fresh water, this has opposite effect of brackish water. To illustrate this, one case has been analyzed where the modeled inside water is that of a full hemisphere. See Figure 27.

Vertical displacement of floater and tarpaulin is plotted in Figure 28. As seen here, the floater raises about 54 cm upwards and the tarpaulin bottom about 7.8 meters.
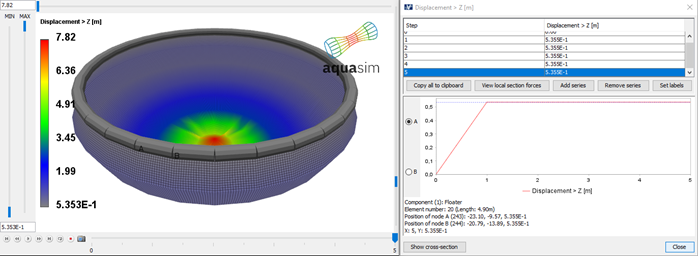
Figure 29 shows the displacement in x-direction, as seen the tarpaulin closed compartment is pushed 2.7 meters sideways in the area below the floater.
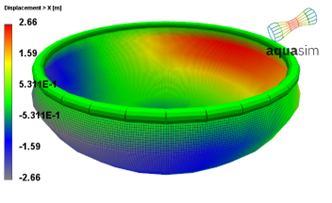
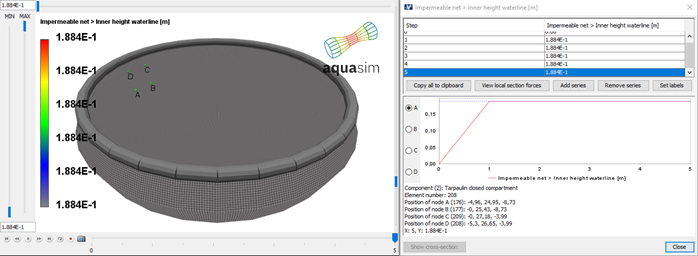
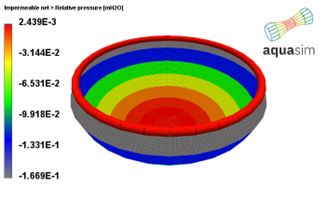
Figure 30 shows, that for this case, the inner waterline is about 18 cm above the outer waterline. Figure 31 shows the relative pressure. As seen here, the relative pressure is slightly inwards along the bottom part of the tarpaulin. The pressure is largely outwards at the upper part. Which is logical with the respective densities and inner water height.